Introduction
Here, I will explain about the uses of 3-tier architecture and how to create and implement 3-tier architecture for our project in ASP.NET.

In the .NET environment, a layer is usually setup as a project that represents this specific function. This specific layer is in charge of working with other layers to perform some specific goal.
Let’s briefly look at the latter situation first.
Though a web site could talk to the data access layer directly, it usually goes through another layer called the business layer. The business layer is vital in that it validates the input conditions before calling a method from the data layer. This ensures the data input is correct before proceeding, and can often ensure that the outputs are correct as well. This validation of input is called business rules, meaning the rules that the business layer uses to make “judgments” about the data.
Client-Server architecture is 2-tier architecture because the client does not distinguish between presentation layer and business layer. The increasing demands on GUI controls caused difficulty to manage the mixture of source code from GUI and Business Logic (spaghetti code). Further, Client Server Architecture does not support enough the Change Management. Let's suppose that the government increases the Entertainment tax rate from 4% to 8 %, then in the Client-Server case, we have to send an update to each client and they must update synchronously on a specific time otherwise we may store invalid or wrong information. The Client-Server Architecture is also a burden to network traffic and resources. Let us assume that about five hundred clients are working on a data server, then we will have five hundred ODBC connections and several ruffian record sets, which must be transported from the server to the clients (because the Business layer is stayed in the client side). The fact that Client-Server does not have any caching facilities like in ASP.NET, caused additional traffic in the network. Normally, a server has a better hardware than client therefore it is able to compute algorithms faster than a client, so this fact is also an additional pro argument for the 3-Tier Architecture. This categorization of the application makes the function more reusable easily and it becomes too easy to find the functions which have been written previously. If programmer wants to make further update in the application, then he easily can understand the previous written code and can update easily.
Let's start creating a 3 architecture application:
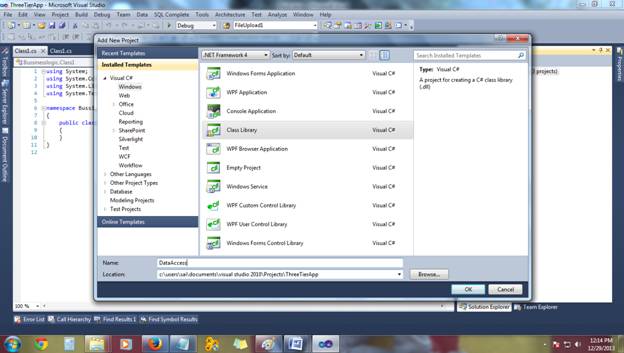
After adding your solution would look like this:

Now we have completed Add all layers to our Project.
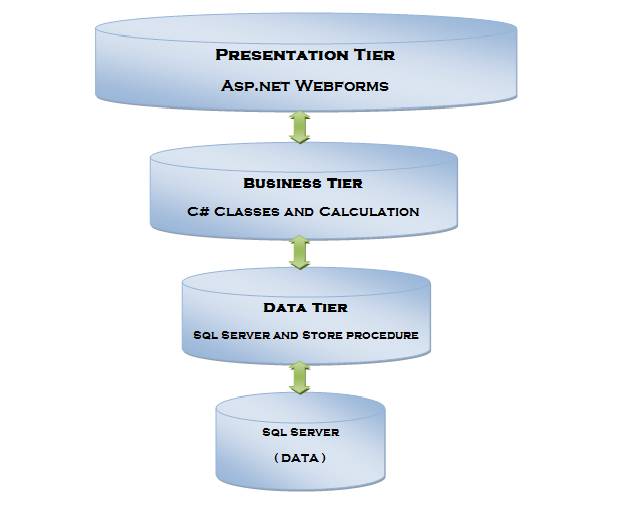
You can see three tiers in the image given below:

Basically 3-Tier architecture contains 3 layers:

Here is the design of (Userregistration.aspx):
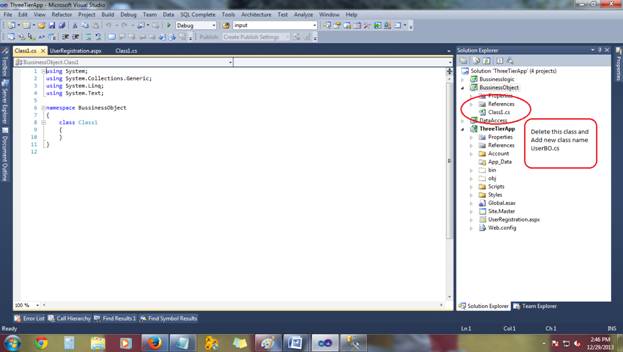
Delete Class
Create New class Name (UserBO.cs):

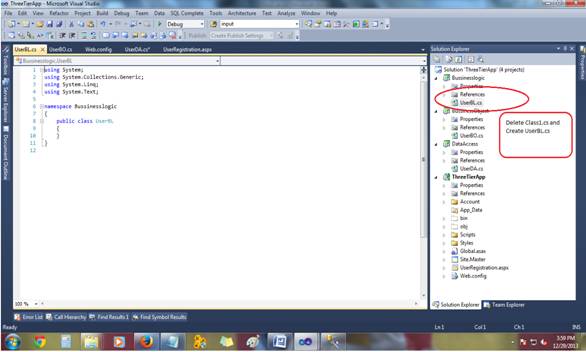
Now same way as we created UserDA.cs,
Main thing TO DO:
We add three layers:
Let's connect them.



What is a Layer?
A layer is a reusable portion of code that performs a specific function.In the .NET environment, a layer is usually setup as a project that represents this specific function. This specific layer is in charge of working with other layers to perform some specific goal.
Let’s briefly look at the latter situation first.
Data Layer
DAL contains methods that help business layer to connect the data and perform required action, might be returning data or manipulating data (insert, update, delete, etc.).Business Layer
BAL contains business logic, validations or calculations related with the data,Though a web site could talk to the data access layer directly, it usually goes through another layer called the business layer. The business layer is vital in that it validates the input conditions before calling a method from the data layer. This ensures the data input is correct before proceeding, and can often ensure that the outputs are correct as well. This validation of input is called business rules, meaning the rules that the business layer uses to make “judgments” about the data.
Presentation Layer
Presentation layer contains pages like .aspx or Windows form where data is presented to the user or input is taken from the user. The ASP.NET web site or Windows forms application (the UI for the project) is called the presentation layer. The presentation layer is the most important layer simply because it’s the one that everyone sees and uses. Even with a well structured business and data layer, if the presentation layer is designed poorly, this gives the users a poor view of the system.Advantages of Three Tier Architecture
The main characteristic of a Host Architecture is that the application and databases reside on the same host computer and the user interacts with the host using an unfriendly and dump terminal. This architecture does not support distributed computing (the host applications are not able to connect a database of a strategically allied partner). Some managers found that developing a host application take too long and it is expensive. Consequently led these disadvantages to Client-Server architecture.Client-Server architecture is 2-tier architecture because the client does not distinguish between presentation layer and business layer. The increasing demands on GUI controls caused difficulty to manage the mixture of source code from GUI and Business Logic (spaghetti code). Further, Client Server Architecture does not support enough the Change Management. Let's suppose that the government increases the Entertainment tax rate from 4% to 8 %, then in the Client-Server case, we have to send an update to each client and they must update synchronously on a specific time otherwise we may store invalid or wrong information. The Client-Server Architecture is also a burden to network traffic and resources. Let us assume that about five hundred clients are working on a data server, then we will have five hundred ODBC connections and several ruffian record sets, which must be transported from the server to the clients (because the Business layer is stayed in the client side). The fact that Client-Server does not have any caching facilities like in ASP.NET, caused additional traffic in the network. Normally, a server has a better hardware than client therefore it is able to compute algorithms faster than a client, so this fact is also an additional pro argument for the 3-Tier Architecture. This categorization of the application makes the function more reusable easily and it becomes too easy to find the functions which have been written previously. If programmer wants to make further update in the application, then he easily can understand the previous written code and can update easily.
Let's start creating a 3 architecture application:
- Create a new project File -> New --> Project.
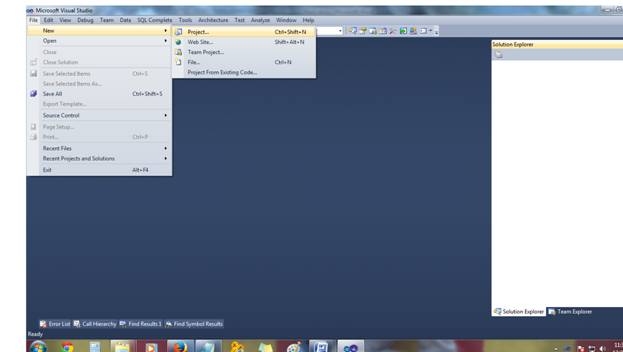
- In Visual C#, select Web
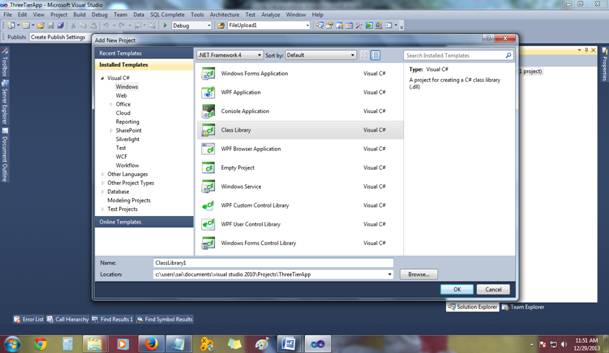
(Select ASP.NET Web application name it as:ThreeTierApp) - How to Add Class Library to solution:
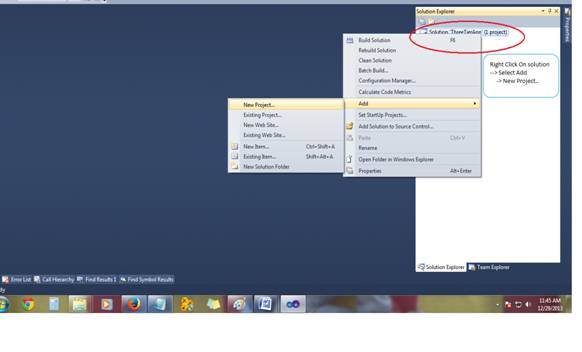
After Clicking on new project, you would see this screen.
- Select Class Library from this and name it as (
BussinessObject):

- Give the name of Class library as
BussinessObject:

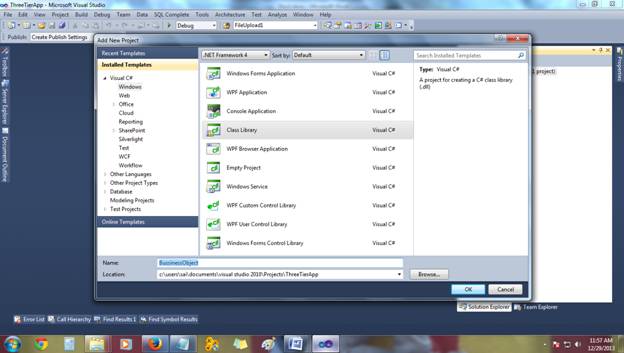
- Add another Class Library to our Project (As the same way you add
BussinessObject): - Name Class library as
Bussinesslogic. - After adding, you will see like this view:

- Adding Last Class library to our project known as Data Access Layer.
- In the same way, you add
BussinessObject. - Name the Class library to
DataAccess:

After adding your solution would look like this:

Now we have completed Add all layers to our Project.
You can see three tiers in the image given below:

Basically 3-Tier architecture contains 3 layers:
- Application Layer or Presentation Layer (our web form and UI Part)
- Business Logic Layer (
Bussinesslogic) - Data Access Layer (
DataAccess)
Presentation Layer
Here I have Design User Interface for (Presentation Layer):
Here is the design of (Userregistration.aspx):
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml">
<head runat="server">
<title></title>
</head>
<body>
<form id="form1" runat="server">
<div style="margin: 0px auto; padding-left: 370px; padding-right: 30px;
overflow: auto;">
<div>
<table width="50%">
<tr>
<td colspan="2" style="background-color: Green; height: 30px;
color: White;" align="center">
User Registration
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td> Name </td>
<td>
<asp:TextBox ID="txtname" Width="150px" runat="server"></asp:TextBox>
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>
Address </td>
<td>
<asp:TextBox ID="txAddress" Width="150px" runat="server"></asp:TextBox>
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td> EmailID </td>
<td>
<asp:TextBox ID="txtEmailid" Width="150px" runat="server"></asp:TextBox>
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td> Mobile Number </td>
<td>
<asp:TextBox ID="txtmobile" Width="150px" runat="server"></asp:TextBox>
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td align="center" colspan="2">
<asp:Button ID="BtnSave" runat="server" Width="100px" Text="Save"
OnClick="BtnSave_Click" />
</td>
</tr>
</table>
</div>
</div>
</form>
</body>
</html>
Now let’s start to create Table for saving this data using (3 tier):CREATE table Userinfo
(
userid bigint primary key not null identity(1,1),
Name Nvarchar(50),
Address Nvarchar(100),
EmailID Nvarchar(50),
Mobilenumber varchar(10)
)
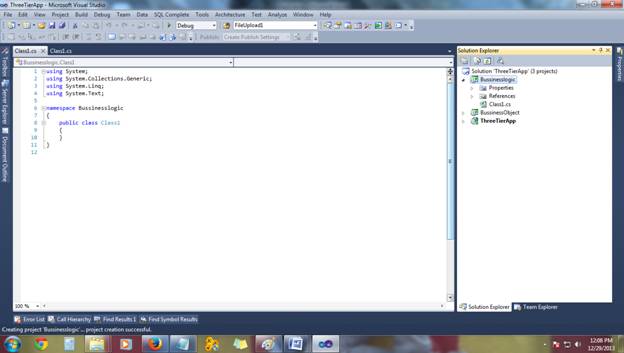
Let's start with Business object first.Delete Class
Class1.Create New class Name (UserBO.cs):

Creating UserBO.cs
Then declare variables in UserBO.cs:using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
namespace BussinessObject
{
Public class UserBO // Declare Class Public to Access any where
{
//Declaring User Registration Variables
private string _Name;
private string _Address;
private string _EmailID;
private string _Mobilenumber;
// Get and set values
public string Name
{
get
{
return _Name;
}
set
{
_Name = value;
}
}
public string address
{
get
{
return _Address;
}
set
{
_Address = value;
}
}
public string EmailID
{
get
{
return _EmailID;
}
set
{
_EmailID = value;
}
}
public string Mobilenumber
{
get
{
return _Mobilenumber;
}
set
{
_Mobilenumber = value;
}
}
}
}
Now in the same way as we created UserBO.cs, create New Class UserDA.cs in (DataAccess):
- In DataAccess
- We are going to use this layer for commutating with database.
- All (
Insert,Update,Delete, selecting records)
Now same way as we created UserDA.cs,
Create New Class UserBL.cs in ( Bussinesslogic )

Main thing TO DO:
We add three layers:
- UserBO.cs
- UserBL.cs
- UserDA.cs
Let's connect them.
First Right Click on (DataAccess)
- Click Add Reference tab
- Select Project
- Inside that, you will see all Layer Name.
- Select (
BussinessObject) from that and Click ok
Second Right Click on (Bussinesslogic)
- Click Add Reference tab
- Select Project
- Inside that, you will see all Layer Name.
- Select (
DataAccess) from that and Click ok
Now, rebuild all layers.
Last step
- Right click on Project add reference
- Click Add Reference tab
- Select Project
- Inside that, you will see all Layer Name.
- Select all add click ok
Now, build project.
UserDA.cs (adding Records)
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Data; // Required for using Dataset , Datatable and Sql
using System.Data.SqlClient; // Required for Using Sql
using System.Configuration; // for Using Connection From Web.config
using BussinessObject; // for acessing bussiness object class
namespace DataAccess
{
public class UserDA
{
SqlConnection con = new
SqlConnection(ConfigurationManager.ConnectionStrings["Myconstr"].ToString());
public int AddUserDetails(UserBO ObjBO) // passing Bussiness object Here
{
try
{
/* Because We will put all out values from our (UserRegistration.aspx)
To in Bussiness object and then Pass it to Bussiness logic and then to
DataAcess
this way the flow carry on*/
SqlCommand cmd = new SqlCommand("sprocUserinfoInsertUpdateSingleItem", con);
cmd.CommandType = CommandType.StoredProcedure;
cmd.Parameters.AddWithValue("@Name", ObjBO.Name);
cmd.Parameters.AddWithValue("@Address", ObjBO.address);
cmd.Parameters.AddWithValue("@EmailID", ObjBO.EmailID);
cmd.Parameters.AddWithValue("@Mobilenumber", ObjBO.Mobilenumber);
con.Open();
int Result = cmd.ExecuteNonQuery();
return Result;
con.close(); //closing connection
}
catch
{
throw;
}
finally
{
cmd.Dispose();
ObjBO.Dispose(); // disposing object
}
}
}
}
UserBL.cs
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using DataAccess; // for acessing DataAccess class
using BussinessObject; // for acessing bussiness object class
namespace Bussinesslogic
{
public class UserBL
{
public int SaveUserregisrationBL(UserBO objUserBL) // passing Bussiness object Here
{
try
{
UserDA objUserda = new UserDA(); // Creating object of Dataccess
return objUserda.AddUserDetails(objUserBL); // calling Method of DataAccess
}
catch
{
throw;
}
}
}
}
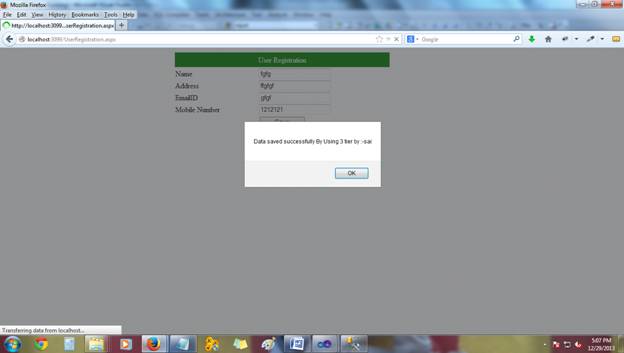
The final output is as follows:
SELECT * FROM Userinfo



